
The average cost of auto insurance in the United States is $1,451 per year or $121 per month. Auto insurance is an important type of insurance coverage that is required by law for drivers in almost every state. According to the Insurance Research Council, approximately 87% of drivers carry auto insurance.
Auto insurance provides financial protection for drivers and car owners in the event that they are involved in a car crash, or if their vehicle is damaged. There are three main coverages in auto insurance: liability, collision, and comprehensive. Liability coverage provides financial protection for drivers if they are at fault for a crash. It can help pay for medical bills and loss of income for injuries caused by an insured driver. It can also provide financial compensation for damages to other vehicles or other property. Collision coverage provides financial protection for a vehicle if it is damaged in a crash, and comprehensive coverage provides financial protection for a vehicle if it is stolen or damaged by something other than a crash, such as theft or flood.
Average Cost of Auto Insurance by State
There is a wide variance in auto insurance costs by state. Our review of state auto insurance costs found that the average annual cost in the cheapest state was only $939 in Maine, while the average cost was as high as $2,154 in Louisiana.
| State | Average Monthly Cost | Average Annual Cost | Difference from National Average |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $108 | $1,302 | -10% |
| Alaska | $115 | $1,378 | -5% |
| Arizona | $120 | $1,441 | -1% |
| Arkansas | $111 | $1,328 | -9% |
| California | $119 | $1,434 | -1% |
| Colorado | $130 | $1,561 | 8% |
| Connecticut | $134 | $1,605 | 11% |
| Delaware | $143 | $1,714 | 18% |
| District of Columbia | $159 | $1,905 | 31% |
| Florida | $152 | $1,825 | 26% |
| Georgia | $138 | $1,659 | 14% |
| Hawaii | $95 | $1,143 | -21% |
| Idaho | $84 | $1,002 | -31% |
| Illinois | $102 | $1,225 | -16% |
| Indiana | $89 | $1,064 | -27% |
| Iowa | $84 | $1,012 | -30% |
| Kansas | $99 | $1,182 | -19% |
| Kentucky | $112 | $1,339 | -8% |
| Louisiana | $180 | $2,154 | 48% |
| Maine | $78 | $939 | -35% |
| Maryland | $136 | $1,633 | 12% |
| Massachusetts | $128 | $1,533 | 6% |
| Michigan | $164 | $1,972 | 36% |
| Minnesota | $100 | $1,205 | -17% |
| Mississippi | $117 | $1,403 | -3% |
| Missouri | $107 | $1,284 | -11% |
| Montana | $106 | $1,272 | -12% |
| Nebraska | $97 | $1,165 | -20% |
| Nevada | $142 | $1,705 | 17% |
| New Hampshire | $91 | $1,094 | -25% |
| New Jersey | $155 | $1,861 | 28% |
| New Mexico | $114 | $1,367 | -6% |
| New York | $158 | $1,902 | 31% |
| North Carolina | $89 | $1,062 | -27% |
| North Dakota | $87 | $1,038 | -28% |
| Ohio | $91 | $1,094 | -25% |
| Oklahoma | $113 | $1,360 | -6% |
| Oregon | $110 | $1,325 | -9% |
| Pennsylvania | $114 | $1,365 | -6% |
| Rhode Island | $153 | $1,830 | 26% |
| South Carolina | $126 | $1,510 | 4% |
| South Dakota | $91 | $1,086 | -25% |
| Tennessee | $101 | $1,215 | -16% |
| Texas | $140 | $1,674 | 15% |
| Utah | $107 | $1,288 | -11% |
| Vermont | $86 | $1,034 | -29% |
| Virginia | $97 | $1,168 | -20% |
| Washington | $114 | $1,366 | -6% |
| West Virginia | $111 | $1,327 | -9% |
| Wisconsin | $83 | $996 | -31% |
| Wyoming | $100 | $1,194 | -18% |
A number of factors can influence the cost of auto insurance in each state. Some of the most important factors are the types of vehicles in each state, the average cost of medical care, the frequency and severity of crashes, exposure to natural disaster damage, and the rate of automobile theft and vandalism. The court system in each state also has an influence on insurance rates, with states awarding higher value damages leading to higher premiums. The number of uninsured motorists in a state can also affect auto insurance premiums.
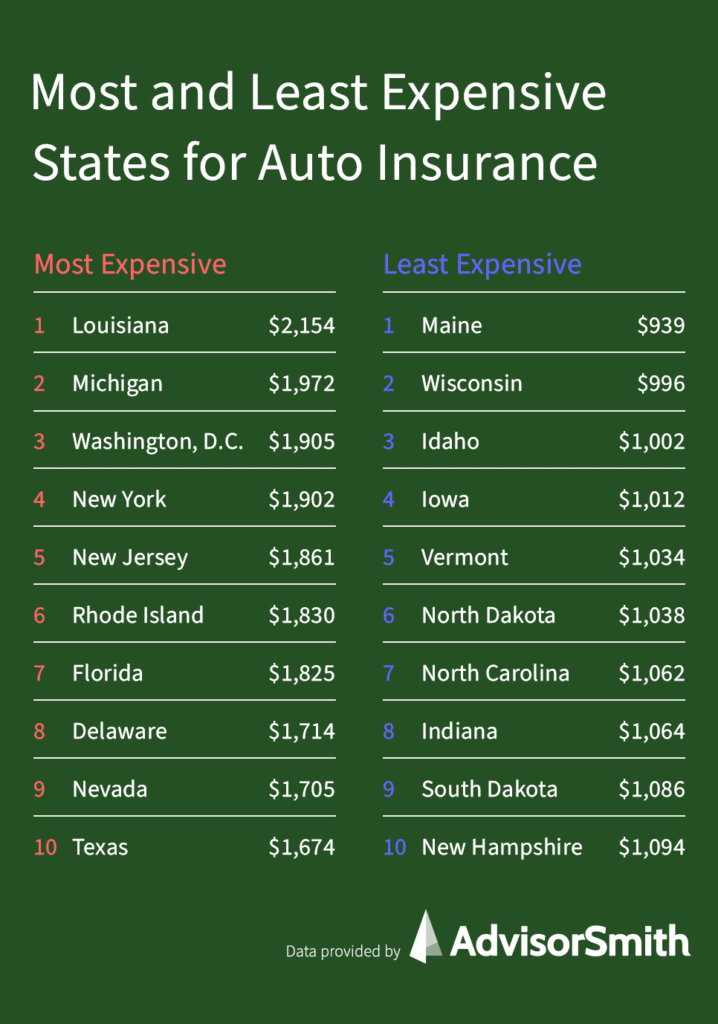
Most Expensive States for Auto Insurance
- Louisiana, with an average annual cost of $2,154
- Michigan, with an average annual cost of $1,972
- Washington, D.C., with an average annual cost of $1,904
- New York, with an average annual cost of $1,901
- New Jersey, with an average annual cost of $1,860
Louisiana topped the list for highest annual cost for car insurance. One factor in Louisiana’s high costs may be the susceptibility of cars in the state to hurricane and flood damage. With a history of hurricanes, drivers in the state may pay more to insure their vehicles. Michigan was the second-highest cost state, possibly due to the state’s no-fault insurance system. The next three spots were taken by New York, New Jersey, and the nation’s capital, all places with high incomes, expensive vehicles, and densely populated metropolitan areas.
Least Expensive States for Auto Insurance
- Maine, with an average annual cost of $939
- Wisconsin, with an average annual cost of $996
- Idaho, with an average annual cost of $1,002
- Iowa, with an average annual cost of $1,012
- Vermont, with an average annual cost of 1,033
All five states where auto insurance is least expensive are states with low population densities and small populations in general. One of the most important factors in the cost of car insurance is the likelihood that a driver will get into a car crash. The fewer people around when driving, the less likely a driver will crash into someone else. These states benefit from reduced density and population, which helps to reduce the costs of auto insurance premiums.
Average Cost of Auto Insurance by City
In the following table, we list the average cost of auto insurance in 25 of the largest cities nationwide. Among these cities, residents of Detroit, Michigan, paid the highest auto insurance premiums, with average rates of $2,791 annually. Rates were cheapest in Charlotte, North Carolina, with the average premium being $1,036 in the city.
| City | Average Monthly Cost | Average Annual Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Austin, Texas | $133 | $1,592 |
| Boston, Massachusetts | $143 | $1,720 |
| Charlotte, North Carolina | $86 | $1,036 |
| Chicago, Illinois | $110 | $1,320 |
| Columbus, Ohio | $96 | $1,152 |
| Dallas, Texas | $149 | $1,788 |
| Denver, Colorado | $162 | $1,948 |
| Detroit, Michigan | $233 | $2,791 |
| El Paso, Texas | $126 | $1,514 |
| Fort Worth, Texas | $141 | $1,692 |
| Houston, Texas | $150 | $1,794 |
| Indianapolis, Indiana | $88 | $1,058 |
| Jacksonville, Florida | $152 | $1,822 |
| Los Angeles, California | $175 | $2,101 |
| Nashville, Tennessee | $102 | $1,224 |
| New York, New York | $177 | $2,129 |
| Oklahoma City, Oklahoma | $122 | $1,464 |
| Philadelphia, Pennsylvania | $175 | $2,104 |
| Phoenix, Arizona | $135 | $1,621 |
| San Antonio, Texas | $136 | $1,634 |
| San Diego, California | $149 | $1,789 |
| San Francisco, California | $180 | $2,159 |
| San Jose, California | $150 | $1,798 |
| Seattle, Washington | $119 | $1,431 |
| Washington, D.C. | $159 | $1,905 |
What’s covered by auto insurance, and what’s not?
Auto insurance provides financial protection for drivers and car owners for several types of incidents. Available coverage includes liability protection in the event that a driver injures another person or damages someone else’s vehicle or property. Other coverages include collision coverage, which protects the value of a vehicle in the event of a crash. Comprehensive coverage provides financial protection in the event that a vehicle is damaged by a non-crash cause.
Some causes of loss are specifically excluded from auto insurance policies. Common exclusions from liability policies include injury or property damage that is intentionally caused by the insured person, damage to property owned by the insured person, and damage while a vehicle is being used for certain commercial purposes, such as delivery or livery businesses, and racing. Comprehensive and collision coverages often exclude damage from wear and tear, mechanical failures, freezing, tire damage, and intentional damage.
The following are some of the key coverages of auto insurance policies:
- Liability Coverage. This coverage is mandatory in most states and provides financial protection in the event of a crash in which the insured driver is at fault. There are usually two components to liability coverage: bodily injury liability and property damage liability. Bodily injury liability helps pay for medical bills, lost wages, and other damages to a person whom a driver has injured in a crash. Property damage liability helps to pay for damages to other vehicles or other property such as buildings, mailboxes, or other structures.
- Collision Coverage. Collision coverage helps to pay the cost to repair or replace a vehicle in the event it is damaged in a crash or collision. If a vehicle is leased or financed, oftentimes this coverage will be required by the lender or finance company. This coverage will pay for the value of the vehicle minus any depreciation. A deductible usually applies to collision damage, which is a portion of the loss that the owner is responsible for.
- Comprehensive Coverage. Comprehensive coverage provides protection against non-crash damage to a vehicle. This damage may be caused by theft, fire, windstorms, vandalism, falling trees or objects, or many other causes. Comprehensive coverage is also commonly required if a vehicle is leased or financed. It also covers the value of the vehicle minus any depreciation and deductible that applies.
- Uninsured and Underinsured Motorist Coverage. On average, one in eight drivers is uninsured in the United States. If a driver without insurance or without adequate insurance hits a vehicle, uninsured and underinsured motorist coverage can provide funds for medical bills, lost wages, and pain and suffering for the driver and their passengers.
- Medical Payments Coverage. Medical payments coverage provides a limited amount of funds to cover medical bills for a driver and their passengers after a crash, regardless of who caused the crash.
- Personal Injury Protection. This coverage is mandatory in no-fault states. It can provide coverage for medical expenses and other expenses such as child care expenses or lost income after a crash.
What determines the cost of auto insurance?
A variety of factors can affect the cost of auto insurance. Drivers should take stock of what coverages are available and determine what coverage they need. It’s also important to shop around between different auto insurance carriers to see which one offers the best coverage for the best value. Some of the most impactful determinants of auto insurance premiums include:
- Driving Record. Drivers with a clean driving record will pay lower premiums. Drivers who have had multiple crashes or other types of traffic violations such as red light tickets, speeding tickets, or DUIs will pay higher premiums. Additionally, new drivers also face higher than average premiums.
- Coverages and Limits of Insurance. While liability insurance is required in most states, many of the other coverages such as collision and comprehensive are optional. While it is a good idea to purchase these coverages, they do cost more. Also, drivers can choose the dollar limits of liability that they wish to have on their policies. The higher the limits of liability, the higher the premiums.
- Deductibles. Another important choice for insurance policyholders is the deductible, which is the amount of a loss that they will be responsible for in the event of a claim. A higher deductible leads to lower premiums, but it also means that the policyholder will shoulder more of the financial risk in the event of a crash or a theft.
- Type of Vehicle. The type of vehicle driven has a major impact on the collision and comprehensive premiums, as the more expensive a vehicle is, the higher the premiums will be. In addition, certain types of vehicles such as sports cars may be more likely to have crashes, so liability premiums may also be higher for these vehicle owners.
- Miles Driven Per Year. Insurance companies generally ask for the number of miles driven annually. If drivers have fewer than average miles driven, they may qualify for discounts based on usage.
- Location. Urban areas with higher rates of theft and vandalism may have higher premiums due to the enhanced losses experienced by auto owners in these neighborhoods. Additionally, the rate of vehicle crashes also varies based upon the neighborhood, and insurance companies may charge higher rates in these locations.
- Age and Gender. Younger drivers, especially those aged 25 or younger, generally face higher premiums. Additionally, young men typically face higher rates than young women due to higher losses among this demographic group.
- Credit Score. In most states, insurance companies are allowed to consider credit scores in insurance pricing. People with higher credit scores can receive discounts from many insurance companies, as their risk models show that people with high credit scores are less likely to be involved in a crash.
Methodology
AdvisorSmith examined data published by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC), which reports on the average premiums paid for auto insurance by drivers around the country. This data, published in February 2021, reported premiums for auto insurance for calendar years 2014-2018. Included in this data set are average premiums paid by drivers in all 50 states and the District of Columbia.
Additionally, AdvisorSmith examined rate quote estimates for auto insurance for drivers from insurers located around the country. We examined average rate quotes for a male driver, 38 years of age, with good credit, driving a 6-year old sedan with a clean driving record. We used the database of rate quote samples, along with data from the NAIC to produce a composite estimate of average auto insurance rates across the country. These quotes included coverage for liability, collision, and comprehensive, with limits of $100,000 per person, $300,000 per crash in bodily injury liability, and $100,000 per crash in property damage liability.


